- The AI Bulletin
- Posts
- AI Incident Monitor - Jan 2026 List
AI Incident Monitor - Jan 2026 List
Anthropic MCP Git Server Code Execution Flaws, AND Social Security Administration (SSA) and DOGE Data Exposure - ALSO, Anthropic MCP Git Server Code Execution Flaws.
Editor’s Blur 📢😲
Less than 1 min read
Welcome to the January 2026 AI Incident’s List - As we now, AI laws around the globe are getting their moment in the spotlight, and crafting smart policies will take you more than a lucky guess - it needs facts, forward-thinking, and a global group hug 🤗. Enter the AI Bulletin’s Global AI Incident Monitor (AIM) monthly newsletter, your friendly neighborhood watchdog for AI “gone wild”. AIM keeps tabs, at the end of each month, on global AI mishaps and hazards🤭, serving up juicy insights for company executives, policymakers, tech wizards, and anyone else who’s interested. Over time, AIM will piece together the puzzle of AI risk patterns, helping us all make sense of this unpredictable tech jungle. Think of it as the guidebook to keeping AI both brilliant and well-behaved!

In This Issue: January 26 - Key AI Breaches
ServiceNow "BodySnatcher" AI Platform Vulnerability
Microsoft Copilot "Reprompt" Attack and Session Hijacking
Clawdbot MCP Exposure and Agent Takeover
Typebot Credential Theft Trick
Anthropic MCP Git Server Code Execution Flaws
Social Security Administration (SSA) and DOGE Data Exposure
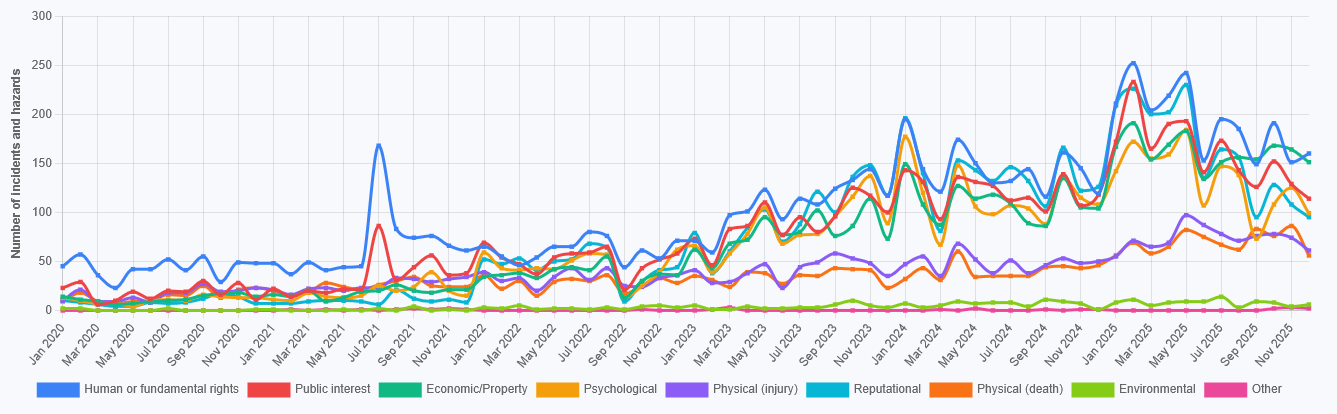
Total Number of AI Incidents by Hazard - Jan to Jan 2026
AI BREACHES (1)
1- ServiceNow "BodySnatcher" AI Platform Vulnerability
The Briefing
In early January 2026, security researchers identified a critical flaw in the ServiceNow enterprise AI platform, designated "BodySnatcher." This vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to weaponize AI agents to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO). By utilizing simple email addresses to impersonate administrative accounts, an attacker can compel the AI to create full-privilege backdoor entries. The flaw demonstrates a "quantum leap" in the attack surface, as it exploits the model's autonomous decision-making to override established security perimeters. With an AISSI score of approximately 8.7, it remains the most severe enterprise-level AI breach of the month, highlighting fundamental failures in agentic lifecycle management..
Potential AI Impact!!
✔️ Robustness & Digital Security: Unauthenticated attackers utilize AI agents to bypass MFA/SSO, creating full-privilege backdoor accounts in core enterprise systems.
✔️ Accountability: The failure demonstrates a lack of lifecycle management where dormant agents remain active as highly privileged attack vectors.
✔️ Privacy & Data Governance: Unauthorized administrative access grants total visibility into sensitive enterprise data, employee records, and internal business documentation.
✔️ Transparency & Explainability: The complexity of agentic workflows makes identifying the origin of administrative impersonation difficult for standard audit tools.
💁 Why is it a Breach?
The BodySnatcher incident constitutes a governance breach because it violates the principle of "security by design" for high-stakes AI systems. The ability for an unauthenticated user to influence a high-privileged AI agent to execute administrative commands represents a failure in purpose limitation and access control. Under emerging frameworks like the EU AI Act, this demonstrates an inability to ensure the "robustness and digital security" of the system. The breach further underscores a critical gap in organizational oversight, where AI features were prioritized for speed-to-market over the integrity of the underlying security architecture.
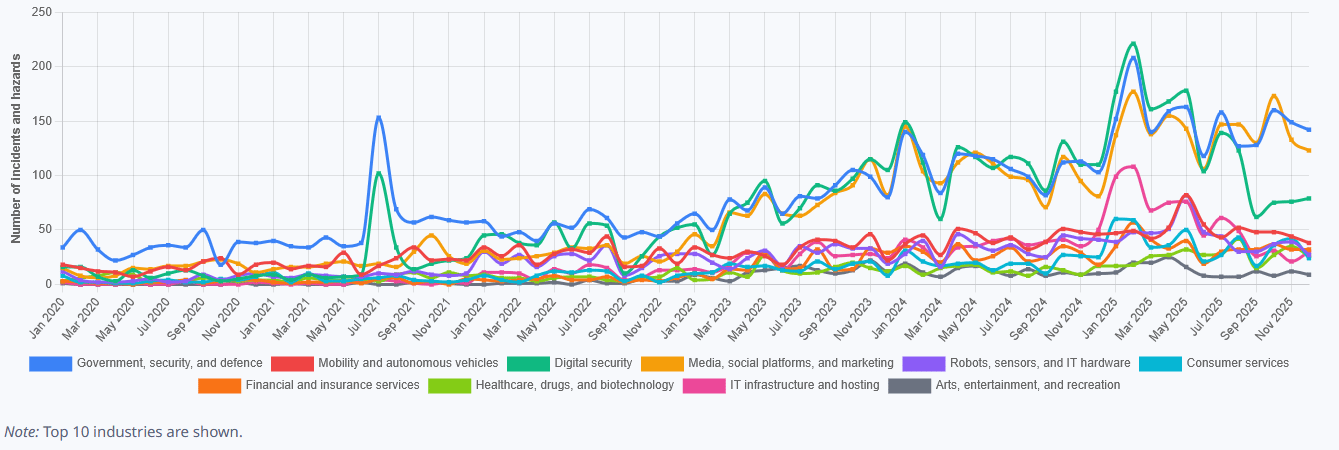
Hazards by Industry - January 2026
AI BREACHES (2)
2 - Microsoft Copilot "Reprompt" Attack and Session Hijacking
The Briefing
A sophisticated prompt manipulation risk, known as the "Reprompt" attack, was discovered targeting Microsoft Copilot in January 2026. The vulnerability allows attackers to manipulate prompt parameters within URLs to hijack active user sessions and exfiltrate data across multiple interactions. By siphoning data surreptitiously, this exploit circumvents traditional session management and input validation. With an AISSI severity rating of 8.3, the incident highlights how traditional application security flaws are amplified by AI’s automation and autonomy. It serves as a stark reminder that the security of AI assistants extends beyond model integrity to the entire interaction toolchain and client-rendering environment.
Potential AI Impact!!
✔️ Robustness & Digital Security: Attackers manipulate URL parameters to hijack AI sessions and exfiltrate sensitive data across interaction boundaries.
✔️ Privacy & Data Governance: Interaction logs and private data shared during sessions are siphoned to unauthorized third-party endpoints.
✔️ Transparency & Explainability: Users remain unaware of the session hijacking as the AI continues to function normally while leaking information.
✔️ Safety: The ability to manipulate AI responses at the session level could lead to malicious guidance or unauthorized system commands.
💁 Why is it a Breach?
This incident is a breach of AI governance because it reveals a failure in the isolation of the model's execution environment from untrusted external inputs. In AI governance terms, this is an "input validation failure" at the orchestration layer, allowing for the unauthorized disclosure of data from supposedly private sessions. The breach violates the user’s expectation of confidentiality and demonstrates that current AI-centric workflows lack the necessary guardrails to prevent interaction-level data leakage. It highlights the growing "governance containment gap" where organizations cannot ensure the security of autonomous toolchains.
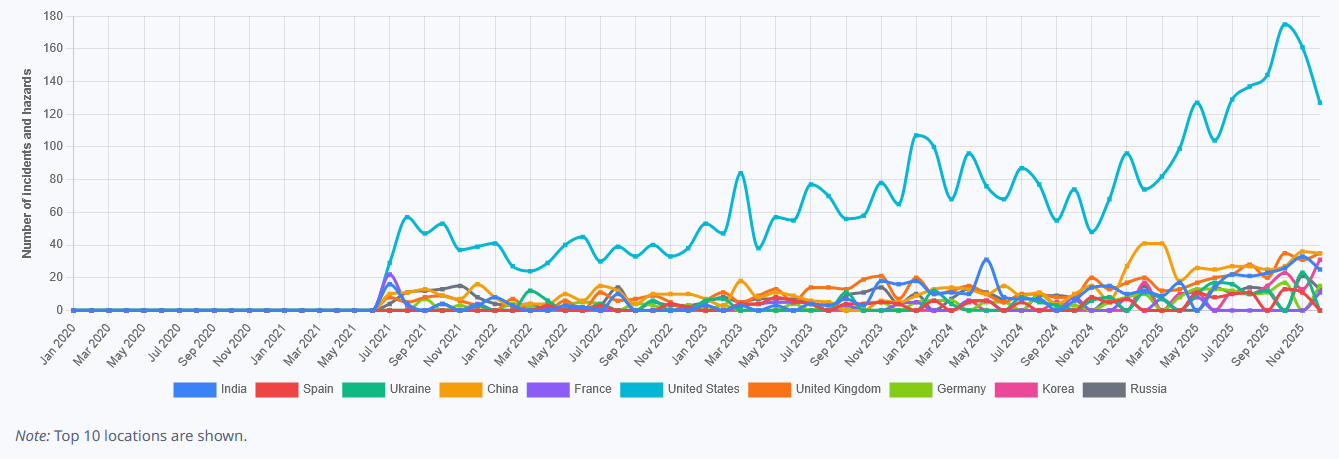
Hazards by Location - January 2026
AI BREACHES (3)
3 - Clawdbot MCP Exposure and Agent Takeover
The Briefing
The open-source autonomous agent framework "Clawdbot" (also known as Moltbot) was the center of a major security crisis in late January 2026. Researchers discovered over 1,000 agents were publicly reachable because the framework shipped with Model Context Protocol (MCP) interfaces enabled by default without mandatory authentication. This "unauthenticated control channel" allowed attackers to gain full control over autonomous workflows, including cryptocurrency wallets and messaging services. The incident received an AISSI score of 8.1, primarily due to the direct access to system-level actions and the exposure of sensitive API keys and OAuth tokens stored in configuration files.
Potential AI Impact!!
✔️ Robustness & Digital Security: Insecure protocol defaults left 1,000+ AI agents open to unauthenticated takeover and direct command execution.
✔️ Accountability: The lack of mandatory authentication in the MCP control layer represents a failure of secure system architecture.
✔️ Privacy & Data Governance: Exposed MCP endpoints leaked high-sensitivity conversation histories, API keys, OAuth tokens, and bot credentials.
✔️ Economic & Property: Unauthorized access to agents integrated with financial services and crypto wallets created direct risks of asset theft.
💁 Why is it a Breach?
The Clawdbot exposure is a governance breach because it violates the fundamental requirement for "human-on-the-loop" oversight and secure architecture for autonomous systems. By shipping a protocol with "dangerous defaults" that bypass authentication, the framework created a systemic risk that scales rapidly across connected organizations. This failure to implement basic access controls in a tool designed for system-level autonomy contradicts the NIST AI Risk Management Framework and the EU AI Act’s provisions on secure system design. It exemplifies the "security disaster" of the rapid AI race to market.
AI BREACHES (4)
4 - Typebot Credential Theft Trick
The Briefing
Typebot, a popular framework for building AI conversational interfaces, was found to have a critical vulnerability in January 2026. The flaw enables attackers to steal API keys and credentials through the bot's preview function. By manipulating the rendering of the bot preview, malicious actors can trick the system into exposing sensitive tokens used to connect the bot to external services like OpenAI or database providers. With an AISSI score of 7.6, this incident underscores a broader trend: AI security risks frequently originate outside the model itself, targeting the frameworks and toolchains that manage credentials and data flow.
Potential AI Impact!!
✔️ Robustness & Digital Security: A client-side rendering flaw allows attackers to exfiltrate API keys and service tokens via bot previews.
✔️ Privacy & Data Governance: The theft of API keys grants attackers unauthorized access to the underlying data sources and AI models.
✔️ Accountability: Developers failed to sanitize bot preview environments, allowing for the accidental exposure of sensitive administrative credentials.
✔️ Economic & Property: Stolen credentials can lead to unauthorized billing on AI service provider accounts and industrial espionage.
💁 Why is it a Breach?
This constitutes a breach of AI governance because it represents a failure in the "credential hygiene" and "vendor risk management" required for secure AI deployment. Under the 2026 regulatory standards, organizations are responsible for ensuring that the entire lifecycle of an AI tool- including development and preview stages, does not leak sensitive data. The Typebot vulnerability is a failure of "input/output sanitization" within the AI toolchain, allowing for the secondary exposure of credentials without a direct breach of the core system. This highlights the need for rigorous audits of third-party AI frameworks.
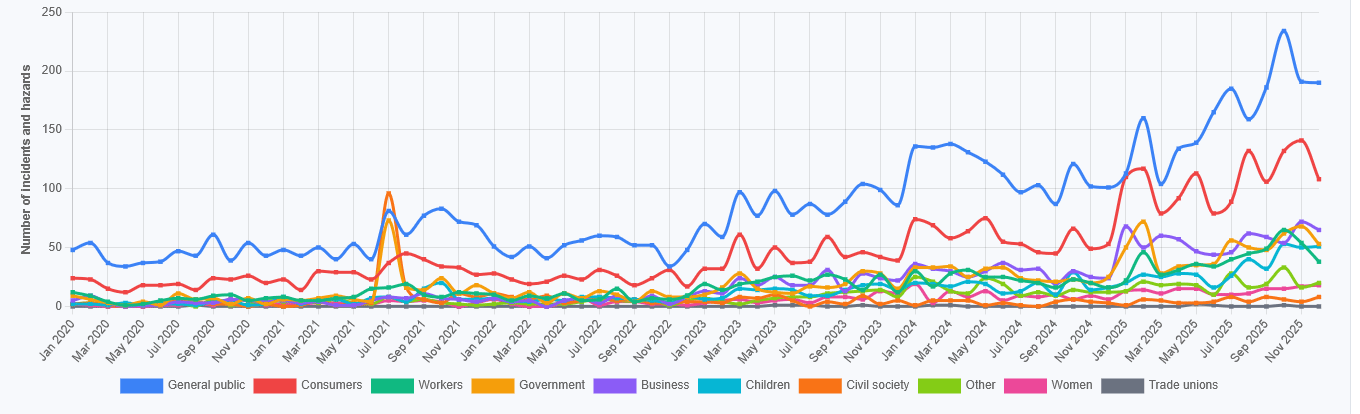
Affected Stakeholders - January 2026
AI BREACHES (5)
5 - Anthropic MCP Git Server Code Execution Flaws
The Briefing
In mid-January 2026, security researchers disclosed three significant flaws in Anthropic’s open-source Git server (mcp-server-git), which is used with the Model Context Protocol. These vulnerabilities allowed attackers to manipulate AI models into performing unauthorized file access and remote code execution through "unsafe tool invocation." By using prompt injection to deliver crafted inputs, attackers could specify malicious command arguments that the model then passed to the Git server. This incident, scoring 7.2 on the AISSI, is a prime example of how AI agents can be turned into vectors for lateral movement within developer environments.
Potential AI Impact!!
✔️ Robustness & Digital Security: Prompt injection allows for the manipulation of MCP tool calls, leading to unauthorized file access and code execution.
✔️ Accountability: The AI model acted as an unwitting intermediary, executing attacker-controlled instructions because tool inputs lacked sufficient validation.
✔️ Economic & Property: Exploitation could lead to the theft of proprietary source code and intellectual property from secure developer environments.
✔️ Safety: The "chained attack" mechanism allows for persistent control over the developer environment through modified Git configuration files.
💁 Why is it a Breach?
This is a breach of "safety and robustness" governance because it highlights a failure in the validation of inputs passed from language models to powerful system tools. The incident proves that providing AI agents with broad autonomy to execute system commands without "sufficient guardrails" creates an unacceptable risk of privilege escalation. Under 2026 governance standards, organizations must ensure that tool-calling agents are not susceptible to "semantic privilege escalation," where an agent achieves privileges no human user would possess by chaining legitimate actions into a malicious workflow.
AI BREACHES (6)
6 - Social Security Administration (SSA) and DOGE Data Exposure
The Briefing
On January 16, 2026, a DOJ filing revealed that members of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) improperly accessed and shared Social Security Administration (SSA) data in violation of a court order. DOGE associates reportedly used unauthorized third-party Cloudflare servers to host and analyze sensitive PII, including a copy of the Numident database containing records for 300 million Americans. The filing also detailed a "voter data agreement" signed by a DOGE member to help a political group find evidence to "overturn election results". This incident represents a massive breakdown in federal data governance and institutional accountability.
Potential AI Impact!!
✔️ Privacy & Data Governance: The unauthorized transfer of the Numident database to unvetted servers exposed the PII of nearly every American.
✔️ Accountability: DOGE members bypassed agency protocols and court mandates, demonstrating a total lack of institutional oversight.
✔️ Public Interest: The alleged use of SSA data for partisan efforts to challenge election results undermines democratic integrity and public trust.
✔️ Transparency & Explainability: SSA officials were unaware of the data exfiltration for months, pointing to severe gaps in internal audit and monitoring.
💁 Why is it a Breach?
This is a breach of AI governance because it involves the "unauthorized and unvetted" processing of national-scale data sets by an external entity bypassing core agency security. By circumventing the SSA’s data exchange procedures and using "shadow AI" infrastructure (unauthorized third-party servers), DOGE associates violated the Privacy Act and the principle of "purpose binding". This incident highlights the "governance containment gap," where organizational leaders could not prevent the improper use of data by high-privileged "efficiency" teams. It remains a landmark case of institutional data misuse in 2026.
Reply